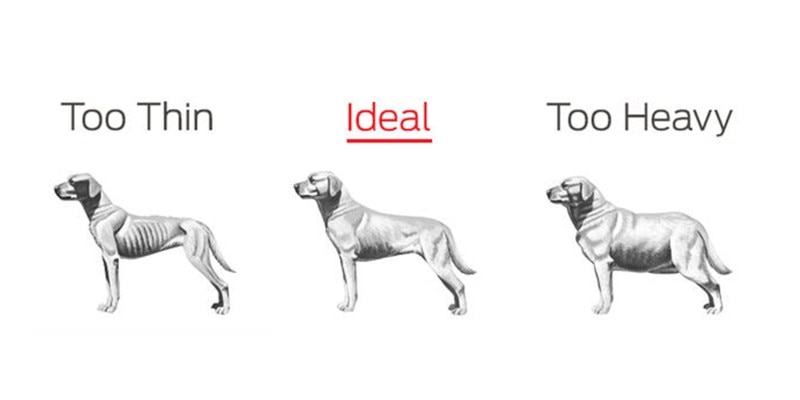
Dog Health: Symptoms & Issues
As a responsible dog owner, it's important to be able to identify the common symptoms of illness in your furry companion. Whether it's coughing and sneezing, limping or difficulty breathing, recognizing these signs early on can help you take proactive measures to ensure your pet stays healthy and receives timely medical attention. Browse our dog symptoms and issues articles from Purina Experts to learn more about what to look out for and how to provide the best possible care for your beloved pet.